Satellite Accumulation Areas
When waste is generated in your classroom, lab, or work space, it is your responsibility to containerize the waste in an appropriate and compatible container and then label the waste and store it in the Satellite Accumulation Area (SAA) for removal. Every lab or area where waste is generated, with a few exceptions, must have an SAA and SAA signage, and under the control of the person/persons generating the waste. SAA rules must be followed at all times:
- Waste must be stored at or near the point of generation
- A lab can have multiple SAAs but the location should be as close to the point of generation as possible. It is best not to transfer large quantities of waste between areas.
- For accumulations of small amounts of hazardous wastes (~4L containers or smaller), a fume hood is considered a practical location.
- For amounts greater than 4L such as a 5-gallon container or 15-gallon plastic drum, an area underneath a counter, “near” a fume-hood, and in a low traffic/low use area are also considered practical.
- Waste storage volume should not exceed 55 gallons per SAA
-
- Once you notice your waste container approaching 80% (leaving room for headspace expansion), please submit a hazardous waste pick-up request.
-
Hazardous Waste Labeling
- Containers must be properly labeled from start of generation.
- Once accumulation of hazardous waste has started, a label must be on the container
with the following information:
- The words “Hazardous Waste,”
- Date of START of accumulation
- Chemical composition (all of the chemicals being added - please use full chemical names, NO abbreviations) and the volume percentage of each chemical (an approximation is okay).
- Generating process
- Check the hazards associated with the waste
- Who it was labeled by (PI name is fine).
- Department and lab phone number
- Building and room where it is generated.
- Once accumulation of hazardous waste has started, a label must be on the container
with the following information:
Hazardous Waste Containers
- Make sure waste is stored in a compatible container
- Consider the type of waste, the amount of waste, and the compatibility of the waste being generated. It may be best to have a 4L glass bottle or a 20L plastic carboy.
- All containers must remain closed at all times except when adding or removing waste.
- If you must use a funnel for the waste container, consider acquiring a safety funnel which can close and seal.
- Containers must be in good condition and not leaking.
- If a container has a lot of chemical residues on the outside or the container begins to leak, the waste can be transferred to a container that is in good condition or over-pack the container that is leaking into a larger, compatible container. A new label should go on the outside of the over-pack container.
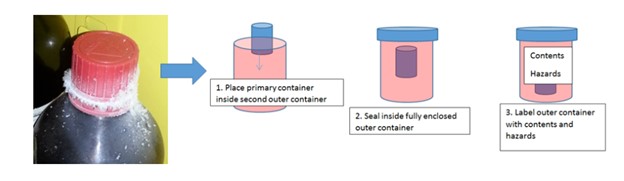
- All waste should be stored in secondary containment
- Secondary containment should be large enough that in the event of a leak or spill of the primary waste container, it should be able to hold all of the primary container contents.
- ALL waste containers MUST be segregated by chemical compatibility
- DO NOT put incompatible chemicals in the same waste container
- ALWAYS CHECK CHEMICAL COMPATIBILITY BEFORE COMBINING OR ADDING NEW OR UNFAMILIAR WASTES INTO THE CONTAINER.
- For liquid wastes: make sure the container is clean and free of contamination, compatible
for the type of waste, and has a leak proof cap.
- Leave a headspace of about 80% to allow for expansion of vapors.
- For dry/solid wastes: make sure the container is clean, free of contamination, and properly tied/taped and sealed.
- For chemically contaminated sharps with no infectious or bio-hazardous contamination: store in a rigid (hard plastic) container with a lid or top that can be sealed with tape.
Central Accumulation Areas
Waste removed from an SAA will be moved to a Central Accumulation Area (CAA), a designated area where hazardous waste is stored by the generator until the waste is removed for disposal, treatment, and/or incineration. Depending on the type of generator, there are specific requirements associated with CAAs, such as storage requirements, storage time limits, and additional emergency response plans and training. If you would like to learn more, please contact the Environmental Program Manager.